Georgia Physical Features Map Labeled: Delving into the geographical tapestry of Georgia, this comprehensive guide unveils the state’s captivating physical attributes. From towering mountains to meandering rivers, verdant valleys to a diverse coastline, Georgia’s natural wonders are showcased with meticulous detail and insightful analysis.
Prepare to embark on a journey that illuminates the defining characteristics of Georgia’s landscape, exploring its geographic regions, water bodies, mountains, valleys, coastal features, climate, vegetation, land use, and natural resources. This exploration promises to deepen your understanding and appreciation of Georgia’s unique physical identity.
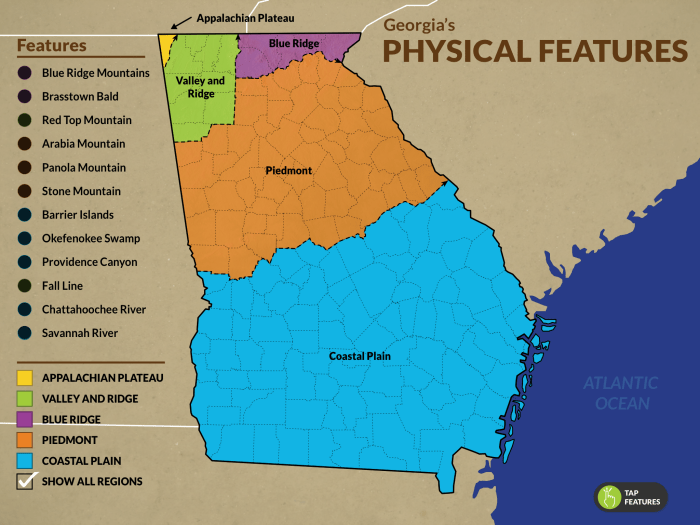
Georgia’s Geographic Regions
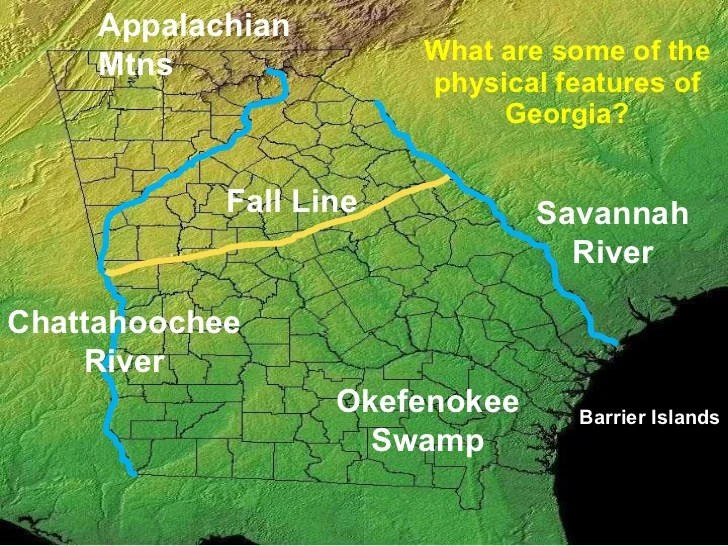
Georgia is a state in the southeastern region of the United States, characterized by diverse geographic features. The state can be divided into five distinct geographic regions, each with its unique characteristics and topography:
- Appalachian Plateau: Located in the northwestern part of Georgia, the Appalachian Plateau is a mountainous region with rugged terrain, steep slopes, and narrow valleys. It is characterized by dense forests and a temperate climate.
- Blue Ridge Mountains: The Blue Ridge Mountains form the eastern border of Georgia and are part of the Appalachian Mountain chain. This region is known for its high peaks, including Mount Yonah and Brasstown Bald, and its scenic beauty.
- Piedmont: The Piedmont region lies between the Appalachian Plateau and the Coastal Plain. It is characterized by rolling hills, fertile valleys, and a mix of forests and farmland. The Piedmont is home to the state’s largest cities, including Atlanta.
- Coastal Plain: The Coastal Plain covers the southern part of Georgia and extends to the Atlantic Ocean. It is a flat, low-lying region with sandy beaches, marshes, and swamps. The Coastal Plain has a subtropical climate and is known for its agriculture, particularly peanuts and cotton.
- Valley and Ridge: The Valley and Ridge region is located between the Appalachian Plateau and the Blue Ridge Mountains. It is characterized by alternating ridges and valleys, with the ridges formed by erosion-resistant sandstone and the valleys formed by softer limestone and shale.
| Region | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Appalachian Plateau | Rugged terrain, steep slopes, narrow valleys, dense forests |
| Blue Ridge Mountains | High peaks, scenic beauty, part of Appalachian Mountain chain |
| Piedmont | Rolling hills, fertile valleys, mix of forests and farmland, largest cities |
| Coastal Plain | Flat, low-lying, sandy beaches, marshes, swamps, subtropical climate, agriculture |
| Valley and Ridge | Alternating ridges and valleys, erosion-resistant sandstone ridges, softer limestone and shale valleys |
Rivers and Lakes
Georgia is home to a diverse network of rivers and lakes that play a crucial role in the state’s geography and economy.
The most significant river in Georgia is the Chattahoochee River, which originates in the Blue Ridge Mountains and flows southwest into Alabama and Florida. Other major rivers include the Savannah River, which forms the border with South Carolina, and the Altamaha River, which is the largest river entirely within Georgia.
Major Rivers
- Chattahoochee River (430 miles): Provides water for drinking, irrigation, and hydroelectric power.
- Savannah River (301 miles): Important for navigation, fishing, and recreation.
- Altamaha River (137 miles): Supports a variety of fish and wildlife, and is used for recreation and irrigation.
- Ocmulgee River (243 miles): Flows through central Georgia and is used for fishing, recreation, and water supply.
- Flint River (345 miles): Provides water for agriculture, industry, and recreation.
Georgia also has several large lakes, including Lake Lanier, Lake Allatoona, and Lake Sinclair. These lakes are popular destinations for fishing, boating, and swimming.
Major Lakes
- Lake Lanier (38,000 acres): Located in north Georgia, it is the largest lake in the state and is used for recreation, water supply, and hydroelectric power.
- Lake Allatoona (12,750 acres): Located in northwest Georgia, it is used for recreation, water supply, and flood control.
- Lake Sinclair (15,330 acres): Located in central Georgia, it is used for recreation, water supply, and hydroelectric power.
Mountains and Valleys
Georgia’s diverse landscape encompasses a range of mountain ranges and valleys that contribute to its scenic beauty and ecological richness.
The mountains of Georgia are primarily located in the northern and northwestern parts of the state, forming a rugged and scenic backdrop to the region.
Mountain Ranges
Georgia’s most notable mountain ranges include:
- Blue Ridge Mountains: The Blue Ridge Mountains extend along the eastern edge of the state, forming the border with North Carolina and Tennessee. They are known for their high peaks, cascading waterfalls, and lush forests.
- Appalachian Mountains: The Appalachian Mountains are a vast mountain system that extends from Canada to Alabama. In Georgia, the Appalachians form the northwestern border with Tennessee and are characterized by rolling hills, deep valleys, and a rich biodiversity.
- Cumberland Plateau: The Cumberland Plateau is a rugged plateau region located in the northwestern part of Georgia. It is known for its sandstone cliffs, deep gorges, and waterfalls.
Valleys
Nestled between the mountain ranges are several valleys that offer a contrasting landscape of rolling hills, fertile farmlands, and picturesque towns.
- Chattahoochee Valley: The Chattahoochee Valley is located in the southwestern part of Georgia, along the Chattahoochee River. It is a fertile agricultural region known for its rolling hills, cotton fields, and peach orchards.
- Coosa Valley: The Coosa Valley is located in the northwestern part of Georgia, along the Coosa River. It is a scenic region with a mix of forests, farms, and small towns.
- Tennessee Valley: The Tennessee Valley is located in the northern part of Georgia, along the Tennessee River. It is a major industrial and agricultural region known for its large cities, dams, and fertile farmlands.
These mountain ranges and valleys contribute to Georgia’s unique and diverse natural heritage, providing a habitat for a wide range of plant and animal species, and offering opportunities for outdoor recreation and tourism.
Coastal Features
Georgia’s coastline stretches for approximately 100 miles (160 km) along the Atlantic Ocean. The coastline is characterized by a series of barrier islands, salt marshes, and tidal creeks. The barrier islands are long, narrow islands that run parallel to the mainland.
They are made up of sand and are constantly being reshaped by the wind and waves.
The salt marshes are located between the barrier islands and the mainland. They are made up of mud and sand and are covered in vegetation. The tidal creeks are channels of water that flow through the salt marshes. They are important for navigation and provide a habitat for a variety of plants and animals.
Major Islands
- St. Simons Island
- Jekyll Island
- Sea Island
- Tybee Island
Beaches
Georgia’s beaches are known for their white sand and gentle waves. They are a popular destination for tourists and locals alike. Some of the most popular beaches include:
- St. Simons Island Beach
- Jekyll Island Beach
- Sea Island Beach
- Tybee Island Beach
Other Coastal Features
In addition to the barrier islands, salt marshes, and beaches, Georgia’s coastline also includes a number of other features. These include:
- Savannah River
- Altamaha River
- Sapelo Island
- Ossabaw Island
Climate and Vegetation
Georgia experiences a diverse range of climates due to its varied topography and location. The state’s climate zones can be broadly classified into three categories: humid subtropical, temperate, and continental.
The humid subtropical climate zone covers most of the southern and central regions of Georgia. This zone is characterized by hot, humid summers and mild winters. The average temperature in July, the warmest month, is around 80°F (27°C), while the average temperature in January, the coldest month, is around 45°F (7°C).
Annual precipitation in this zone averages around 50 inches (127 cm).
The temperate climate zone is found in the northern and mountainous regions of Georgia. This zone experiences warm summers and cool winters. The average temperature in July is around 75°F (24°C), while the average temperature in January is around 35°F (2°C).
Annual precipitation in this zone averages around 40 inches (102 cm).
The continental climate zone is found in the extreme northern part of Georgia. This zone experiences cold winters and warm summers. The average temperature in July is around 70°F (21°C), while the average temperature in January is around 25°F (-4°C).
Annual precipitation in this zone averages around 30 inches (76 cm).
Vegetation, Georgia physical features map labeled
The vegetation of Georgia is closely tied to its climate zones. The humid subtropical climate zone is home to a variety of forests, including oak-hickory forests, pine forests, and cypress swamps. The temperate climate zone is home to deciduous forests, including maple-beech forests and oak-hickory forests.
The continental climate zone is home to coniferous forests, including spruce-fir forests and pine forests.
The vegetation of Georgia plays a vital role in the state’s ecosystem. Forests provide habitat for a variety of animals, including deer, bears, and birds. Forests also help to regulate the state’s water cycle and prevent erosion.
Land Use and Natural Resources: Georgia Physical Features Map Labeled
Georgia’s land use patterns reflect its diverse geography and economy. The state’s major land use categories include forests, agriculture, urban areas, and wetlands. Forests cover approximately 60% of Georgia’s land area, providing timber, wildlife habitat, and recreation opportunities. Agriculture is another major land use, with crops such as cotton, peanuts, and soybeans being grown throughout the state.
Urban areas are concentrated in the Atlanta metropolitan area and other major cities. Wetlands, including marshes, swamps, and bottomlands, cover approximately 10% of Georgia’s land area and provide important habitat for fish and wildlife.
Natural Resources
Georgia is rich in natural resources, including minerals, forests, and water. The state’s mineral resources include granite, marble, limestone, and kaolin. Georgia is also a major producer of timber, with its forests providing lumber, pulpwood, and other wood products. The state’s water resources include rivers, lakes, and aquifers.
The Chattahoochee, Savannah, and Altamaha rivers are major sources of water for drinking, irrigation, and transportation.The state’s natural resources have played a vital role in its economic development. The mining industry has been a major contributor to Georgia’s economy for centuries.
The state’s forests have also been a major source of wealth, providing timber for construction and other purposes. Georgia’s water resources have been essential for the development of agriculture, industry, and transportation.The state’s natural resources are also important for its environment.
Forests help to clean the air and water, and they provide habitat for wildlife. Wetlands help to control flooding and provide habitat for fish and wildlife. Rivers and lakes provide recreation opportunities and support a variety of aquatic life.Georgia’s natural resources are a valuable asset to the state.
They have played a vital role in its economic development and they continue to be important for its environment. The state’s leaders must work to protect and conserve these resources for future generations.
Common Queries
What are the major geographic regions of Georgia?
Georgia’s geographic regions include the Appalachian Plateau, Blue Ridge Mountains, Valley and Ridge Province, Piedmont, and Coastal Plain.
Which is the highest mountain in Georgia?
Brasstown Bald, located in the Blue Ridge Mountains, is the highest mountain in Georgia with an elevation of 4,784 feet.
What is the largest river in Georgia?
The Chattahoochee River is the largest river in Georgia, flowing for 430 miles from its headwaters in the Blue Ridge Mountains to the Gulf of Mexico.
What is the climate like in Georgia?
Georgia has a humid subtropical climate, with hot, humid summers and mild winters. The average temperature in Atlanta, the state capital, ranges from 34°F in January to 84°F in July.
What are the major natural resources in Georgia?
Georgia’s natural resources include forests, minerals, and water. The state is a leading producer of kaolin, granite, and marble. Georgia also has abundant water resources, with major rivers such as the Chattahoochee, Savannah, and Ocmulgee providing water for drinking, irrigation, and transportation.