Steps in human evolution crossword: embark on a captivating journey through time, tracing the remarkable evolution of our species. From the earliest hominids to the emergence of modern humans, this crossword puzzle unravels the intricate tapestry of our origins.
This comprehensive guide delves into the key stages of human evolution, exploring the physical and behavioral characteristics that shaped our ancestors. Discover the significance of bipedalism, tool use, language, and culture in our evolutionary trajectory. Through archaeological evidence and scientific insights, we piece together the puzzle of human evolution, revealing the fascinating story of our past.
1. Human Evolutionary Timeline
Human evolution is a complex and gradual process that has taken place over millions of years. It involves the emergence of modern humans from earlier hominid ancestors and the development of unique physical and behavioral characteristics.
Major Events in Human Evolution
- 6-7 million years ago:Bipedalism (walking upright) emerges in hominids.
- 4-5 million years ago:Australopithecus species appear, exhibiting ape-like features and bipedalism.
- 2-3 million years ago:Homo habilis emerges, with increased brain size and tool-making abilities.
- 1.5-2 million years ago:Homo erectus appears, with larger brain size, controlled fire, and advanced tool use.
- 500,000-200,000 years ago:Homo neanderthalensis emerges in Europe and Asia.
- 200,000-100,000 years ago:Homo sapiens (modern humans) emerge in Africa.
Factors Influencing Human Evolution
- Environmental changes:Climate change, habitat shifts, and competition for resources.
- Natural selection:Traits that enhance survival and reproduction are favored.
- Genetic mutations:Random changes in genetic material can introduce new traits.
- Cultural transmission:Learned behaviors and technologies are passed down through generations.
2. Stages of Human Evolution
Human evolution can be divided into distinct stages, each characterized by unique physical and behavioral traits.
Pre-Hominid Stage
- 6-7 million years ago:Ardipithecus ramidus exhibits bipedalism and knuckle-walking.
- 4-5 million years ago:Australopithecus species display bipedalism and limited tool use.
Early Hominid Stage
- 2-3 million years ago:Homo habilis has increased brain size and tool-making abilities.
- 1.5-2 million years ago:Homo erectus has a larger brain, controlled fire, and advanced tool use.
Late Hominid Stage
- 500,000-200,000 years ago:Homo neanderthalensis exhibits complex social behavior and tool technology.
- 200,000-100,000 years ago:Homo sapiens (modern humans) emerge with advanced cognitive abilities and language.
Evidence for Human Evolution
- Fossil record:Preserved remains of hominid species provide physical evidence of evolutionary changes.
- DNA analysis:Comparisons of DNA sequences reveal genetic similarities and differences among hominid species.
- Archaeological findings:Stone tools, artifacts, and settlements provide insights into hominid behavior and cultural development.
3. Bipedalism and Tool Use
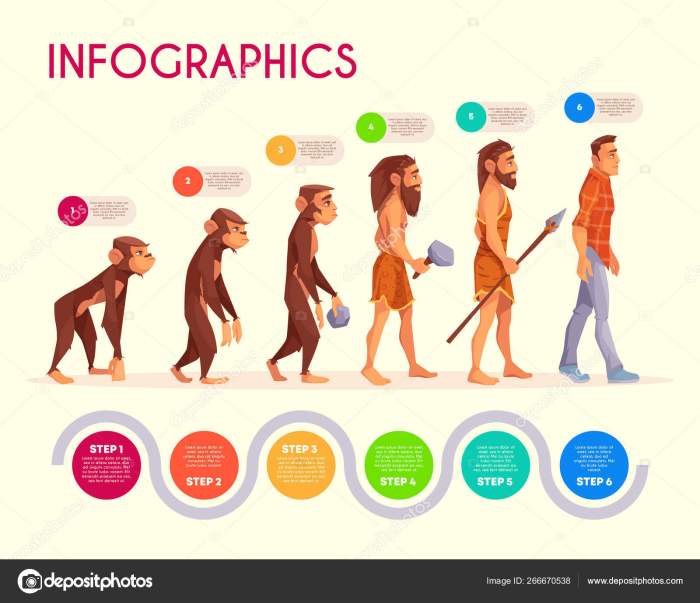
Bipedalism and tool use are two significant milestones in human evolution that have shaped our species’ unique adaptations.
Significance of Bipedalism, Steps in human evolution crossword
- Freed hands for tool use and carrying objects.
- Improved visibility and scanning of the environment.
- Enhanced energy efficiency for long-distance travel.
Tool Use and Its Contributions
- Hunting and gathering efficiency:Tools for cutting, scraping, and hunting improved food acquisition.
- Shelter construction and protection:Tools for building shelters and defending against predators.
- Cognitive development:Tool-making and use stimulated problem-solving and innovation.
Examples of Early Hominid Tools
- Oldowan tools (2.6-1.7 million years ago):Simple stone flakes and cores used for cutting and scraping.
- Acheulean tools (1.7-0.2 million years ago):Handaxes and cleavers for hunting and butchering.
4. Language and Culture

The development of language and culture played a crucial role in the evolution of human society and cognition.
Language Development
- Emergence of symbolic communication:Symbols and sounds to represent objects, actions, and ideas.
- Syntax and grammar:Rules for combining words and phrases into meaningful sentences.
- Complexity and diversity:Language evolved into complex and diverse systems across different human populations.
Role of Culture
- Shared beliefs, values, and practices:Culture provided a framework for social organization and cooperation.
- Transmission of knowledge and skills:Culture allowed for the accumulation and transfer of knowledge across generations.
- Technological innovation and artistic expression:Culture fostered creativity and the development of new technologies and artistic forms.
Evidence for the Emergence of Culture
- Symbolic artifacts:Engraved bones, cave paintings, and jewelry suggest symbolic thinking and artistic expression.
- Burial practices:Intentional burial of the dead indicates social and ritualistic behavior.
- Tool diversity:Variation in tool types and technologies reflects cultural differences and adaptations to specific environments.
Expert Answers: Steps In Human Evolution Crossword
What are the key stages in human evolution?
The key stages in human evolution include Australopithecus, Homo habilis, Homo erectus, Homo neanderthalensis, and Homo sapiens.
What factors influenced human evolution?
Factors that influenced human evolution include climate change, natural selection, and cultural adaptations.
How did bipedalism contribute to human evolution?
Bipedalism freed up the hands for tool use and carrying, allowing for increased mobility and hunting efficiency.
What is the evidence that supports the theory of human evolution?
Evidence supporting the theory of human evolution includes fossil records, DNA analysis, and comparative anatomy.
What are the characteristics that distinguish modern humans from other hominids?
Characteristics that distinguish modern humans from other hominids include larger brains, reduced body hair, and the ability to produce complex language.