Introduction to evidence-based practice edapt – Introducing the transformative concept of evidence-based practice (EBP) in healthcare, this comprehensive guide delves into its evolution, principles, components, and impact on patient care. Through a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical examples, we explore the significance of EBP in shaping healthcare decisions and improving patient outcomes.
Evidence-based practice emerged as a systematic approach to healthcare, emphasizing the integration of research evidence, clinical expertise, and patient values. It has revolutionized the way healthcare professionals make decisions, leading to improved patient care, reduced healthcare costs, and enhanced patient satisfaction.
1. Introduction to Evidence-Based Practice (EBP)
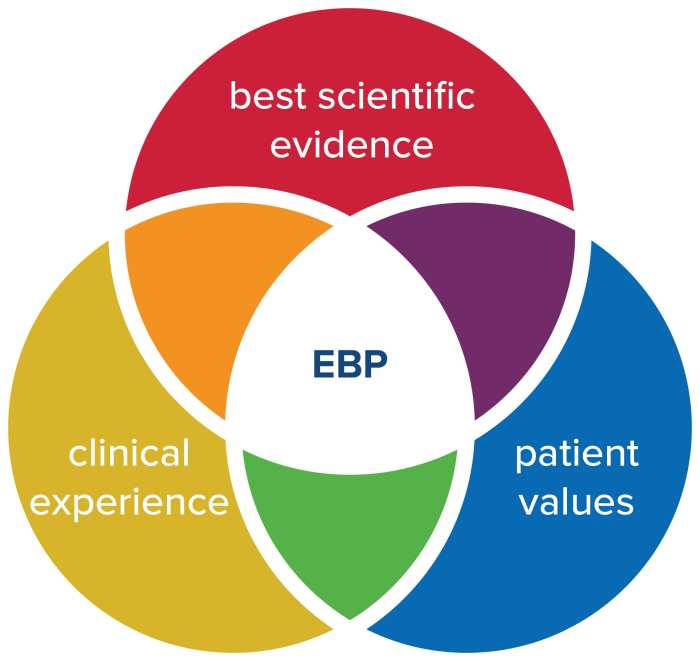
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is a systematic approach to healthcare that uses the best available evidence to make decisions about patient care. It involves using research findings, clinical expertise, and patient preferences to guide practice.
The concept of EBP has been evolving over time, with its roots in the scientific method and the use of clinical research. In the 1990s, EBP gained prominence as a way to improve healthcare quality and outcomes.
Key Principles of EBP
- Use the best available evidence to make decisions about patient care.
- Integrate research findings, clinical expertise, and patient preferences.
- Be systematic and transparent in the process of evaluating and using evidence.
- Continuously evaluate and improve practice based on new evidence.
2. Components of EBP

The EBP process involves five key steps:
Ask
Identify the clinical question or problem that needs to be addressed.
Acquire
Search for and retrieve the best available evidence to answer the question.
Appraise
Critically evaluate the evidence for its validity, reliability, and applicability.
Apply
Integrate the evidence with clinical expertise and patient preferences to make decisions about patient care.
Assess
Evaluate the outcomes of the intervention and make adjustments as needed.
Role of Research Evidence in EBP
Research evidence plays a crucial role in EBP. It provides the foundation for making informed decisions about patient care. Research findings can help to identify effective treatments, interventions, and strategies.
3. Benefits and Challenges of EBP
Benefits of EBP
- Improved patient outcomes
- Reduced healthcare costs
- Increased patient satisfaction
- Enhanced professional practice
Challenges of EBP
- Lack of time and resources
- Difficulty accessing and interpreting research evidence
- Resistance to change
- Cultural and organizational barriers
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges
- Provide training and support for healthcare professionals
- Develop tools and resources to facilitate EBP
- Create a culture that values EBP
- Address organizational barriers
4. EBP in Different Healthcare Settings

EBP can be applied in various healthcare settings, including:
Hospitals
EBP can be used to improve patient care in hospitals, such as reducing hospital-acquired infections, improving medication safety, and managing chronic diseases.
Clinics
EBP can be used in clinics to improve the quality of care for patients with specific conditions, such as diabetes, asthma, and hypertension.
Community Health Centers
EBP can be used in community health centers to address the health needs of underserved populations, such as providing culturally appropriate care and reducing health disparities.
Role of Healthcare Professionals in Promoting EBP, Introduction to evidence-based practice edapt
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in promoting EBP. They can:
- Stay up-to-date on the latest research evidence
- Critically evaluate and apply evidence to their practice
- Collaborate with other healthcare professionals to implement EBP initiatives
- Advocate for policies and practices that support EBP
5. Future of EBP

EBP is a continuously evolving field. Emerging trends and advancements include:
Technology
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in EBP. Electronic health records, clinical decision support systems, and mobile health apps can help healthcare professionals access and use evidence more easily.
Big Data
Big data analytics can be used to identify trends, patterns, and associations in healthcare data. This information can be used to develop more personalized and targeted interventions.
Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine is an approach to healthcare that uses genetic information to tailor treatments to individual patients. EBP is essential for ensuring that personalized medicine is based on the best available evidence.
Predictions for the Future of EBP
EBP is expected to continue to play a vital role in healthcare in the future. As technology advances and our understanding of healthcare improves, EBP will become even more essential for making informed decisions about patient care.
FAQ Resource: Introduction To Evidence-based Practice Edapt
What is the key principle of EBP?
The key principle of EBP is to integrate the best available research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values to make informed healthcare decisions.
What are the five steps of EBP?
The five steps of EBP are: Ask, Acquire, Appraise, Apply, and Assess.
What are the benefits of implementing EBP in healthcare?
The benefits of implementing EBP in healthcare include improved patient outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and enhanced patient satisfaction.