The molarity of FenCS2+ in standard FenCS2+ solution is a fundamental concept in analytical chemistry. Understanding its significance enables precise preparation and utilization of these solutions in various applications. This guide delves into the intricacies of molarity, standard solutions, and the specific case of FenCS2+.
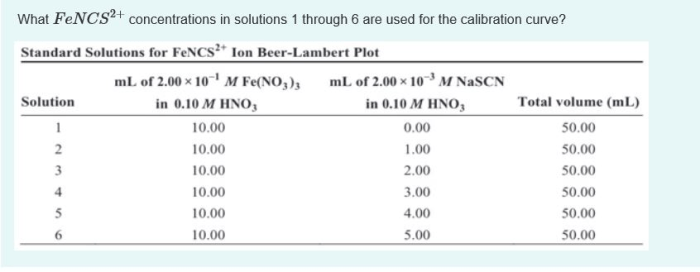
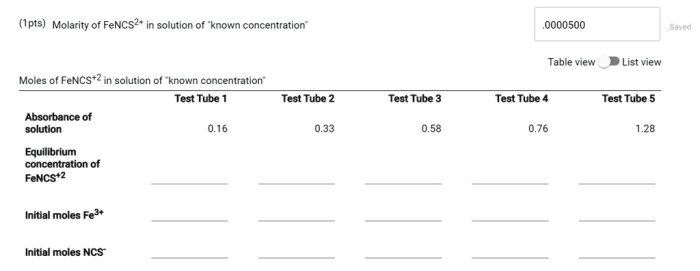
Standard solutions serve as references for determining the concentration of unknown solutions. Preparing a standard solution of FenCS2+ involves dissolving a precisely weighed mass of FenCS2+ in a known volume of solvent. The resulting solution’s molarity is calculated using the formula: Molarity = moles of solute / volume of solution in liters.
Molarity of FenCS2+ in Standard FenCS2+ Solution

Molarity is a measure of the concentration of a solution, defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It is a crucial concept in chemistry, as it allows us to determine the amount of a substance present in a given volume.
Standard solutions are solutions with a precisely known concentration. They are essential in analytical chemistry for various applications, such as titrations and calibrations. Preparing a standard solution of FenCS2+ involves dissolving a known mass of FenCS2+ salt in a known volume of solvent.
Molarity Calculation for FenCS2+ Solutions, Molarity of fencs2+ in standard fencs2+ solution
The formula for calculating molarity is:
M = n/V
where:
- M is the molarity in moles per liter (mol/L)
- n is the number of moles of solute
- V is the volume of the solution in liters (L)
To calculate the molarity of a FenCS2+ solution, we need to know the mass of FenCS2+ salt used and the volume of the solution prepared.
For example, if we dissolve 0.250 g of FenCS2+ in 250 mL of solution, the molarity can be calculated as:
M = (0.250 g / 262.1 g/mol) / (250 mL / 1000 mL/L) = 0.00378 mol/L
Therefore, the molarity of the FenCS2+ solution is 0.00378 mol/L.
Dilution and Preparation of FenCS2+ Solutions
Dilution involves adding more solvent to a concentrated solution to decrease its concentration. To prepare a FenCS2+ solution of a specific molarity, we can dilute a concentrated FenCS2+ solution.
The formula for dilution is:
M1V1 = M2V2
where:
- M1 is the initial molarity
- V1 is the initial volume
- M2 is the final molarity
- V2 is the final volume
For example, to prepare 250 mL of a 0.00100 mol/L FenCS2+ solution from a 0.100 mol/L stock solution, we can use the dilution formula:
0.100 mol/L
- V1 = 0.00100 mol/L
- 250 mL
Solving for V1, we get V1 = 2.5 mL. Therefore, we need to take 2.5 mL of the concentrated solution and add it to 247.5 mL of solvent to obtain a 250 mL solution with a molarity of 0.00100 mol/L.
Applications of FenCS2+ Standard Solutions
FenCS2+ standard solutions have various applications in research and industry, including:
- Electrochemistry:FenCS2+ is used as a redox indicator in electrochemical titrations.
- Analytical chemistry:FenCS2+ standard solutions are used for the quantitative determination of Fe2+ ions in solution.
- Industrial processes:FenCS2+ is used in the production of steel and other alloys.
The molarity of the FenCS2+ standard solution plays a crucial role in these applications, as it determines the accuracy and precision of the measurements or reactions being performed.
Detailed FAQs: Molarity Of Fencs2+ In Standard Fencs2+ Solution
What is the significance of molarity in chemistry?
Molarity is a measure of the concentration of a solution, expressed as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It is a fundamental parameter used in various chemical calculations and analytical techniques.
How is a standard solution of FenCS2+ prepared?
To prepare a standard solution of FenCS2+, a precisely weighed mass of FenCS2+ is dissolved in a known volume of solvent. The molarity is then calculated using the formula: Molarity = moles of solute / volume of solution in liters.
What are the applications of FenCS2+ standard solutions?
FenCS2+ standard solutions are used in various applications, including acid-base titrations, redox reactions, and complexometric titrations. They serve as references for determining the concentration of unknown solutions and are essential in analytical chemistry.