Embark on a scientific odyssey with the practice protein synthesis answer key, a comprehensive guide that demystifies the intricate world of protein synthesis. Dive into the fundamental principles, explore experimental methods, and unravel real-world applications of this essential biological process.
From transcription and translation to the role of ribosomes and tRNA, this resource provides a thorough understanding of the molecular machinery behind protein synthesis. Engage in interactive exercises, delve into laboratory protocols, and witness the transformative power of protein synthesis in biotechnology and medicine.
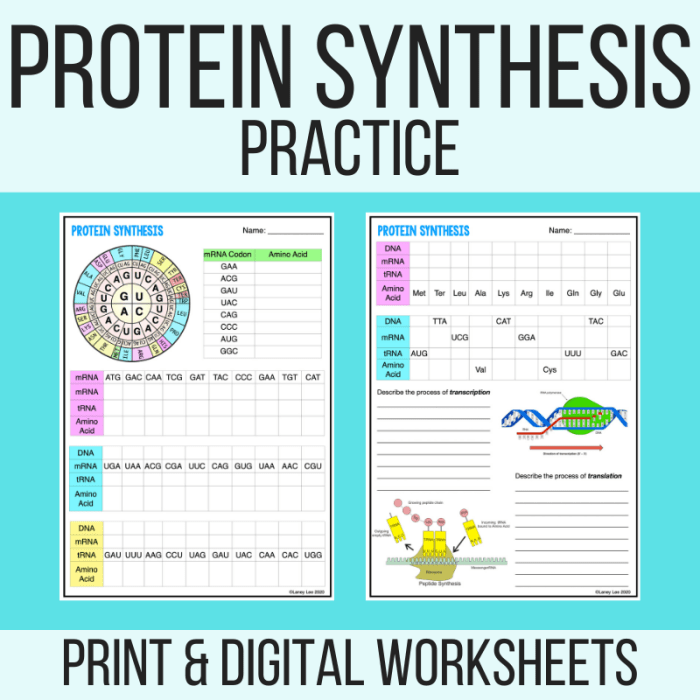
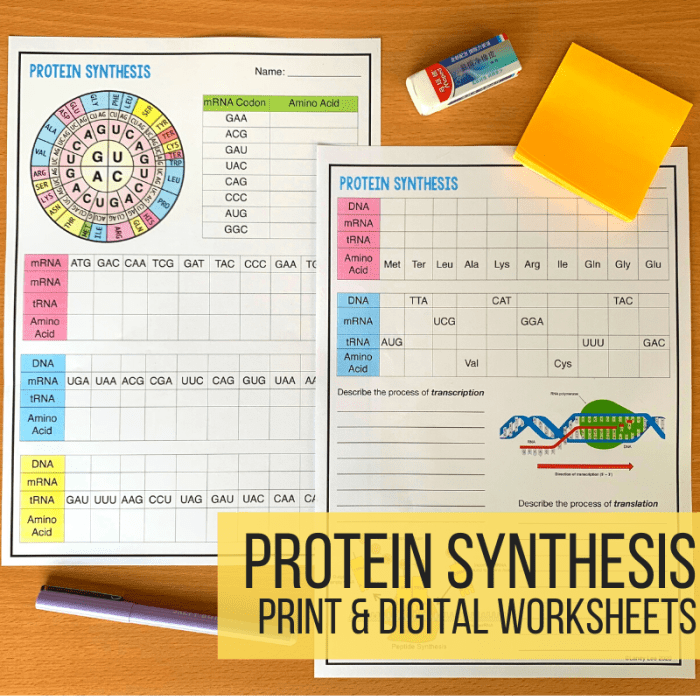
1. Protein Synthesis Overview: Practice Protein Synthesis Answer Key
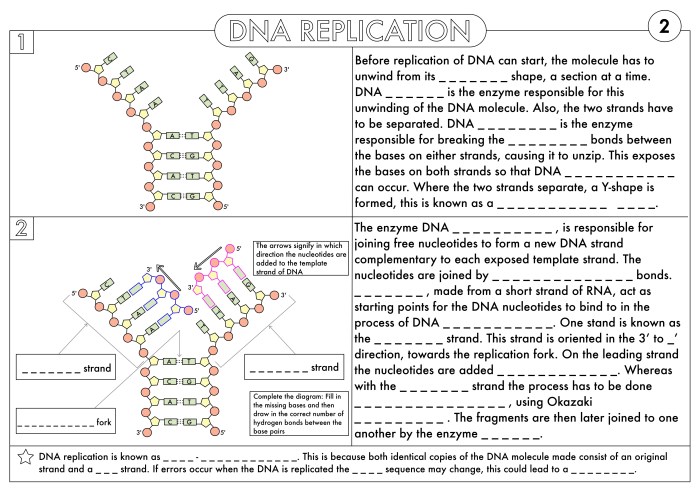
Protein synthesis is the fundamental process by which cells produce proteins, essential macromolecules involved in a wide range of cellular functions. This intricate process consists of two main stages: transcription and translation.
Transcription
During transcription, the DNA sequence of a gene is copied into a complementary messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. This mRNA molecule serves as the template for protein synthesis, carrying the genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
Translation, Practice protein synthesis answer key
In translation, the mRNA molecule is decoded by ribosomes, cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, each carrying a specific amino acid, interact with the mRNA molecule, matching their anticodons with the codons on the mRNA. This matching process allows the correct sequence of amino acids to be assembled, forming the polypeptide chain of the protein.
Role of Ribosomes and tRNA
Ribosomes are the essential machinery for protein synthesis, providing the site for mRNA and tRNA interaction. They catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids, elongating the polypeptide chain. tRNA molecules play a crucial role in decoding the genetic information by recognizing specific codons on the mRNA and delivering the corresponding amino acids to the ribosome.
Detailed FAQs
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
The central dogma describes the unidirectional flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein.
How do ribosomes function in protein synthesis?
Ribosomes are the cellular machinery responsible for assembling amino acids into polypeptide chains based on the genetic code.
What is the role of tRNA in protein synthesis?
tRNA molecules carry specific amino acids to the ribosome, ensuring the correct sequence of amino acids in the growing polypeptide chain.