Match the function with the correct area thalamus or hypothalamus – Match the function with the correct area: thalamus or hypothalamus. The thalamus and hypothalamus are two essential brain regions with distinct functions. The thalamus acts as a relay center for sensory information, while the hypothalamus plays a crucial role in regulating bodily functions.
Understanding the differences between these regions is key to comprehending their significance in brain function.
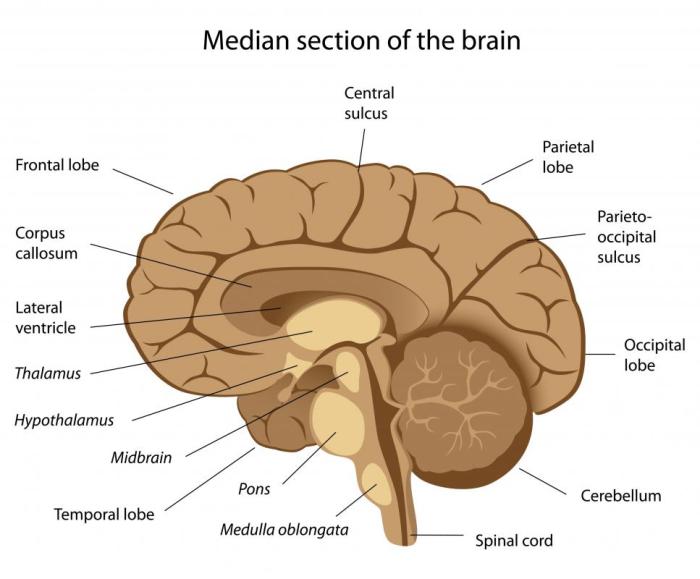
The thalamus, located deep within the brain, serves as a sensory processing center. It receives sensory signals from the body and sends them to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex for further processing. The hypothalamus, situated below the thalamus, is responsible for maintaining homeostasis by regulating body temperature, hunger, thirst, and sleep-wake cycles.
It also controls the release of hormones from the pituitary gland, influencing various bodily functions.
Thalamus
The thalamus is a small structure located at the base of the brain that plays a vital role in relaying sensory information to the cerebral cortex, regulating consciousness and alertness, and controlling motor functions.
Role in Sensory Information Relay
The thalamus serves as a sensory relay center, receiving sensory information from all parts of the body and directing it to the appropriate areas of the cerebral cortex for processing. It filters and processes this information, ensuring that only the most relevant and important signals reach the cortex.
Regulation of Consciousness and Alertness
The thalamus also plays a crucial role in regulating consciousness and alertness. It receives signals from the brainstem and sends them to the cortex, helping to maintain a state of wakefulness and attention. Additionally, the thalamus is involved in the sleep-wake cycle, helping to initiate and maintain sleep.
Control of Motor Functions
The thalamus is connected to the basal ganglia, which are involved in motor control. It helps to coordinate and smooth out voluntary movements, ensuring that they are executed accurately and efficiently.
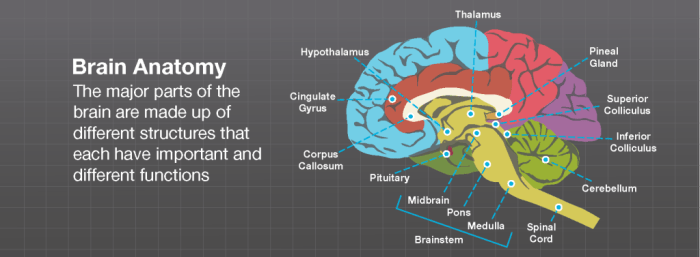
Hypothalamus
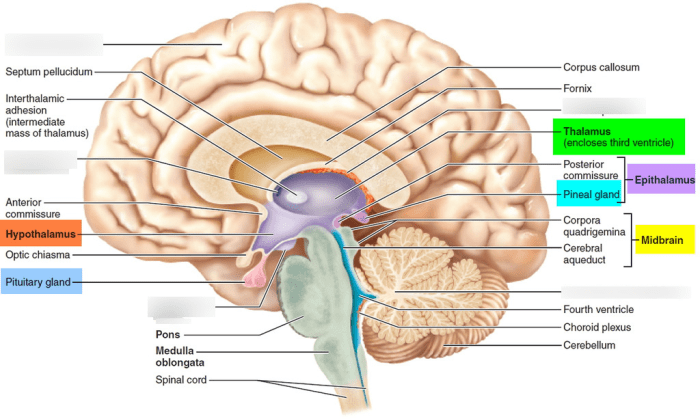
The hypothalamus is a small region located at the base of the brain that is responsible for regulating a wide range of bodily functions, including body temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep-wake cycles, and hormone release.
Regulation of Body Temperature
The hypothalamus acts as the body’s thermostat, maintaining a constant body temperature. It monitors body temperature and sends signals to the appropriate mechanisms to either cool down or warm up the body.
Regulation of Hunger and Thirst
The hypothalamus plays a key role in regulating hunger and thirst. It receives signals from the digestive system and blood glucose levels, and sends signals to the appropriate areas of the brain to stimulate or inhibit eating and drinking.
Control of Hormone Release, Match the function with the correct area thalamus or hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is connected to the pituitary gland, which is responsible for releasing hormones into the bloodstream. The hypothalamus produces releasing hormones that stimulate the pituitary gland to release specific hormones, and inhibiting hormones that prevent the release of hormones.
Comparison of Thalamus and Hypothalamus: Match The Function With The Correct Area Thalamus Or Hypothalamus
| Thalamus | Hypothalamus | |
|---|---|---|
| Key Functions | Sensory relay, consciousness, motor control | Body temperature, hunger, thirst, hormone release |
| Location | Base of the brain | Base of the brain |
| Structure | Two oval-shaped structures | Small, cone-shaped structure |
Similarities
- Both are located at the base of the brain.
- Both are involved in regulating bodily functions.
- Both are connected to the cerebral cortex.
Differences
- The thalamus is involved in relaying sensory information, while the hypothalamus is involved in regulating bodily functions.
- The thalamus is a larger structure than the hypothalamus.
- The thalamus has a more complex structure than the hypothalamus.
Clinical Implications
Dysfunctions of the Thalamus
Dysfunctions of the thalamus can affect sensory processing and consciousness. Damage to the thalamus can lead to sensory deficits, such as numbness or tingling, and can also impair consciousness, leading to coma or vegetative states.
Dysfunctions of the Hypothalamus
Dysfunctions of the hypothalamus can lead to disorders related to body temperature regulation and hormone imbalances. Damage to the hypothalamus can lead to conditions such as hypothermia, hyperthermia, diabetes insipidus, and obesity.
FAQs
What is the primary function of the thalamus?
The thalamus acts as a relay center for sensory information, transmitting signals from the body to the cerebral cortex for processing.
How does the hypothalamus regulate body temperature?
The hypothalamus monitors body temperature and activates mechanisms to maintain optimal levels, such as sweating or shivering.
What hormones are released by the hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus controls the release of hormones from the pituitary gland, including growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and adrenocorticotropic hormone.